Starting ECMO:Cannulation
When preparation is complete, cannulation can take place. The cannulation process for V-V ECMO and peripheral V-A ECMO is carried out using the Seldinger Technique:
- The blood vessel of interest is identified (at TGH the use of ultrasound is often employed).
- A relatively small needle is used to enter the vessel.
- A guidewire is threaded into the blood vessel and the needle is removed.
- Dilators with increasingly large diameters are placed in a stepwise fashion one at a time over the guidewire until the tract is of sufficient size for the cannula to fit.
- The cannula is then placed in the vessel and the distal end is positioned in its desired location (this may be done with real time imaging depending on the location).
- The process is then repeated for the return cannula if necessary.
For central V-A ECMO, the return cannula is placed via a sternotomy and direct placement into the thoracic aorta.
When the cannulas are appropriately placed, they are joined to the ECMO circuit tubing by placing the two ends together while pouring saline over them to ensure no air is entrained into the circuit.
If you see any air in the tubing it is important to bring it to the attention of the surgeons and the perfusionists.
Cannula Verification:
It is important to verify that the cannulas are placed correctly, as this can have a large impact on the hemodynamics. Cannula placement can be verified in the following ways:
- X-ray: real time fluoroscopy can be used during placement, and afterwards standard chest and abdominal x-rays can be used to identify the position of the cannula.
- Transthoracic echocardiography: the cannula position can often be identified by transthoracic echocardiography at the bedside.
- Transesophageal echocardiography: this can be used to verify the position of the cannula, and is especially important when verifying the position of an Avalon catheter to ensure the jet is pointed towards the tricuspid valve.
V-V ECMO Dual Cannulation:
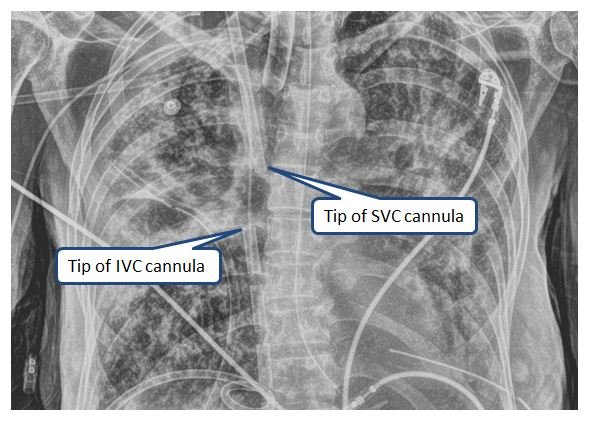
- The drainage cannula is typically placed in a femoral vein and the tip should be positioned in the proximal IVC.
- Cases have been described where the distal end migrates into the hepatic vein, which can have disastrous consequences.
- If the cannula is placed too distally then flow can be limited by the collapse of the IVC.
- The right internal jugular cannula should be positioned in the proximal SVC.
Pictured in the x-ray below are appropriately positioned drainage and return cannulas for Vf-Vj ECMO.
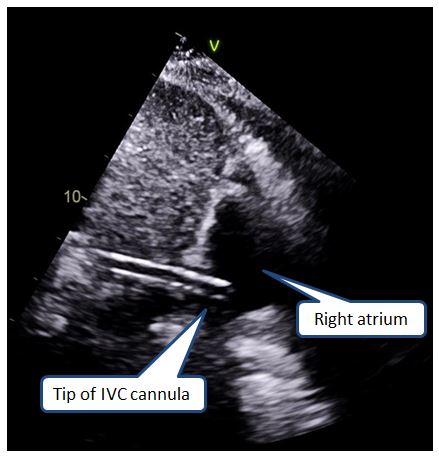
The echocardiogram below demonstrates the drainage cannula in the IVC with the tip in the right atrium.
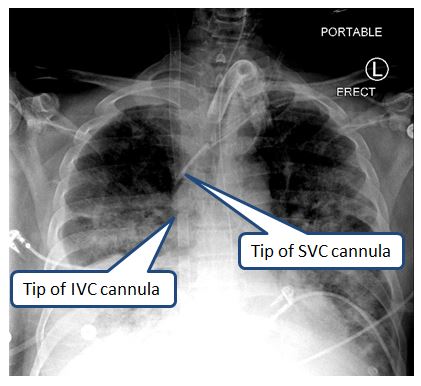
Pictured in the X-ray below is a Vf-Vj ECMO configuration where the cannula position is incorrect. The cannulas are too close together and the drainage cannula is too high:
V-V ECMO Single Cannulation (Avalon):
- This is referred to as (dl)V-V ECMO.
- The cannula should be positioned via the right internal jugular vein so that the return port is in the right atrium and the drainage ports are in the IVC and SVC respectively.
- The flow from the return port must be directed at the tricuspid valve (this requires transesophageal echocardiography).
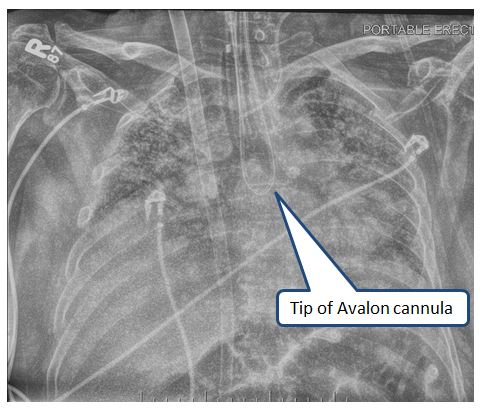
Pictured in the x-ray below is an Avalon cannula which is positioned in the right atrium for (dl)V-V ECMO
V-A ECMO Peripheral Cannulation:
- Just like with V-V ECMO, the venous drainage cannula is typically placed femorally, situated in the proximal IVC.
- The arterial cannula should be placed via the femoral artery and advanced into the abdominal aorta below the level of the renal arteries,
- The distal perfusion should be placed in the distal femoral artery.
Below is an x-ray of a peripheral Vf-Af ECMO configuration. Note that the arterial cannula is not seen, because the distal end is positioned in the abdominal aorta below the renal arteries.
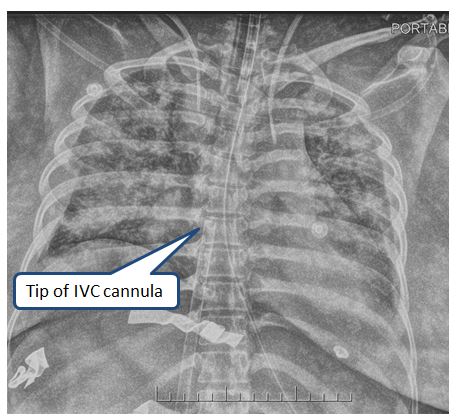
V-A ECMO Central Cannulation:
- Just like with V-V ECMO and peripheral V-A ECMO, the venous drainage cannula is often placed in the proximal IVC via one of the femoral veins.
- It can also be placed centrally directly into the right atrium.
- The arterial return cannula is usually placed in the ascending aorta.
Next page: Daily care of the ECMO patient: Circuit settings
